Beware: The Bacteria Danger Zone
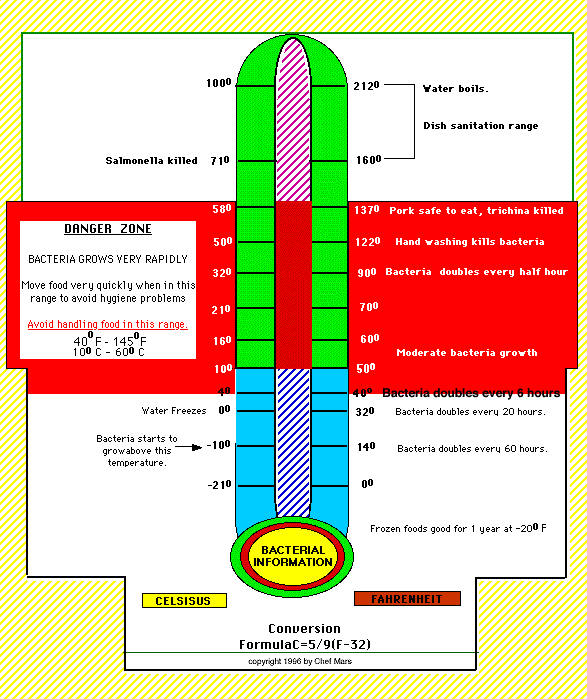
The "bacteria danger zone" refers to the temperature range between 40F and 140F (4C and 60C) in which bacteria can grow and multiply rapidly. This range is particularly concerning because it encompasses temperatures commonly found in kitchens, restaurants, and other food preparation areas.
Keeping food out of the bacteria danger zone is essential for preventing foodborne illness. Bacteria can double in number every 20 minutes in the danger zone, so even a short period of time can lead to significant bacterial growth. To prevent this, foods should be kept at or below 40F or at or above 140F.
There are a number of ways to keep food out of the bacteria danger zone. Refrigerators and freezers should be kept at the proper temperatures, and food should be refrigerated or frozen within two hours of cooking. Hot food should be kept hot until it is served, and cold food should be kept cold until it is eaten. Additionally, food should not be left out at room temperature for more than two hours.
Read also:The Ultimate Guide To Understanding 12 Pm What It Means And How To Use It
Bacteria Danger Zone
The bacteria danger zone refers to the temperature range between 40F and 140F (4C and 60C) in which bacteria can grow and multiply rapidly. This range is particularly concerning because it encompasses temperatures commonly found in kitchens, restaurants, and other food preparation areas.
- Temperature: The danger zone is defined by its temperature range, between 40F and 140F.
- Bacteria growth: Bacteria can double in number every 20 minutes in the danger zone.
- Foodborne illness: Keeping food out of the danger zone is essential for preventing foodborne illness.
- Refrigeration: Refrigerators should be kept at or below 40F to prevent bacteria growth.
- Freezing: Freezing food at or below 0F can prevent bacteria growth.
- Hot holding: Hot food should be kept at or above 140F to prevent bacteria growth.
- Time: Food should not be left out at room temperature for more than two hours.
These key aspects highlight the importance of temperature control in preventing bacterial growth and foodborne illness. By understanding the bacteria danger zone and following safe food handling practices, we can help to ensure that our food is safe to eat.
1. Temperature
The temperature range between 40F and 140F is known as the "bacteria danger zone." This is because bacteria can grow and multiply rapidly in this temperature range. Bacteria can double in number every 20 minutes in the danger zone, which can lead to foodborne illness.
- Growth Rate: Bacteria grow best between 90F and 110F. However, they can still grow slowly at temperatures as low as 40F and as high as 140F.
- Types of Bacteria: Not all bacteria are harmful. However, some types of bacteria, such as Salmonella, E. coli, and Listeria, can cause foodborne illness. These bacteria can grow in the danger zone.
- Foodborne Illness: Foodborne illness is a major public health problem. Each year, millions of people in the United States get sick from eating contaminated food. Bacteria are a common cause of foodborne illness.
- Preventing Foodborne Illness: One of the best ways to prevent foodborne illness is to keep food out of the danger zone. This means refrigerating or freezing food promptly after cooking, and reheating food to a safe internal temperature before eating.
Understanding the bacteria danger zone is essential for preventing foodborne illness. By keeping food out of the danger zone, we can help to keep our food safe to eat.
2. Bacteria Growth
The rapid growth of bacteria in the danger zone is a major concern because it can lead to foodborne illness. Foodborne illness is a common problem, with millions of cases reported each year in the United States alone. Symptoms of foodborne illness can range from mild to severe, and in some cases, can even be fatal.
The bacteria that cause foodborne illness can grow and multiply rapidly in the danger zone. This is because the temperature range between 40F and 140F is ideal for bacterial growth. In fact, bacteria can double in number every 20 minutes in the danger zone.
Read also:How Many Us Fluid Ounces Exactly Constitute A Pint
This rapid growth can lead to a significant increase in the number of bacteria present in food. Even a small amount of bacteria can cause illness, so it is important to keep food out of the danger zone to prevent the growth of bacteria.
There are a number of ways to keep food out of the danger zone. Refrigerators and freezers should be kept at the proper temperatures, and food should be refrigerated or frozen within two hours of cooking. Hot food should be kept hot until it is served, and cold food should be kept cold until it is eaten. Additionally, food should not be left out at room temperature for more than two hours.
By understanding the importance of keeping food out of the danger zone, we can help to prevent foodborne illness and keep our food safe to eat.
Foodborne illness is a major public health concern, with millions of cases reported each year in the United States alone. Bacteria are a common cause of foodborne illness, and the bacteria danger zone is a key factor in the growth and spread of bacteria in food.
Bacteria Danger Zone and Foodborne Illness
Bacteria can grow and multiply rapidly in the temperature range between 40F and 140F, which is known as the bacteria danger zone. This range encompasses temperatures commonly found in kitchens, restaurants, and other food preparation areas. When food is left in the danger zone for too long, bacteria can multiply to levels that can cause foodborne illness.
Keeping Food Out of the Danger Zone
Keeping food out of the danger zone is essential for preventing foodborne illness. There are a number of ways to do this, including:
- Refrigerating or freezing food promptly after cooking
- Reheating food to a safe internal temperature before eating
- Avoiding leaving food out at room temperature for more than two hours
By following these simple steps, you can help to prevent the growth of bacteria and reduce your risk of foodborne illness.
Conclusion
Understanding the bacteria danger zone is essential for preventing foodborne illness. By keeping food out of the danger zone, you can help to keep your food safe to eat.
3. Refrigeration
Refrigeration is one of the most important ways to prevent bacteria growth and keep food safe to eat. The temperature range between 40F and 140F is known as the "bacteria danger zone." In this temperature range, bacteria can grow and multiply rapidly, doubling in number every 20 minutes.
Keeping refrigerators at or below 40F helps to prevent bacteria from growing and multiplying. This is because bacteria need a warm environment to grow, and the cold temperature of the refrigerator slows down their growth.
There are a number of foods that are particularly susceptible to bacteria growth, including:
- Meat
- Poultry
- Seafood
- Dairy products
- Eggs
These foods should be refrigerated or frozen within two hours of cooking or thawing.
It is also important to keep the refrigerator clean. Spills should be cleaned up immediately, and the refrigerator should be cleaned thoroughly once a week.
By following these simple tips, you can help to prevent bacteria growth and keep your food safe to eat.
4. Freezing
Freezing food at or below 0F can prevent bacteria growth because bacteria need a warm environment to grow and multiply. The cold temperature of the freezer slows down the growth of bacteria, and at 0F, bacteria cannot grow at all.
Freezing food is an important way to prevent foodborne illness. Foodborne illness is a common problem, with millions of cases reported each year in the United States alone. Bacteria are a common cause of foodborne illness, and freezing food can help to prevent the growth of bacteria and reduce the risk of foodborne illness.
There are many different types of bacteria that can cause foodborne illness. Some of the most common include Salmonella, E. coli, and Listeria. These bacteria can grow in a variety of foods, including meat, poultry, seafood, dairy products, and eggs.
Freezing food can help to prevent the growth of these bacteria and reduce the risk of foodborne illness. However, it is important to note that freezing food does not kill bacteria. If food is thawed and then left at room temperature, bacteria can begin to grow again. Therefore, it is important to keep frozen food frozen until it is ready to be cooked or eaten.
Freezing food is a safe and effective way to prevent bacteria growth and reduce the risk of foodborne illness. By following these simple tips, you can help to keep your food safe to eat.
5. Hot holding
Hot holding is a food safety practice that involves keeping hot food at or above 140F to prevent the growth of bacteria. This is important because bacteria can grow rapidly in the temperature range between 40F and 140F, which is known as the "bacteria danger zone."
- Preventing Bacterial Growth: Hot holding helps to prevent the growth of bacteria by keeping food out of the bacteria danger zone. Bacteria need a warm environment to grow, and the high temperature of hot holding makes it difficult for bacteria to survive.
- Reducing the Risk of Foodborne Illness: Foodborne illness is a major public health concern, and hot holding can help to reduce the risk of foodborne illness by preventing the growth of bacteria that can cause food poisoning.
- Maintaining Food Quality: Hot holding can also help to maintain the quality of food. Food that is kept hot is less likely to spoil and will retain its flavor and texture better than food that is kept in the bacteria danger zone.
- HACCP Compliance: Hot holding is a critical component of HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points), a food safety system that is used to prevent foodborne illness. HACCP requires that hot food be held at or above 140F to prevent the growth of bacteria.
Hot holding is an important food safety practice that can help to prevent the growth of bacteria, reduce the risk of foodborne illness, and maintain the quality of food. By following hot holding guidelines, foodservice establishments can help to ensure that the food they serve is safe to eat.
6. Time
Food should not be left out at room temperature for more than two hours because the bacteria danger zone is between 40F and 140F. In this temperature range, bacteria can grow and multiply rapidly, doubling in number every 20 minutes. This can lead to foodborne illness, which is a major public health concern.
Leaving food out at room temperature for more than two hours gives bacteria time to grow and multiply to dangerous levels. This is especially true for foods that are high in protein, such as meat, poultry, and dairy products. These foods provide a good environment for bacteria to grow.
To prevent foodborne illness, it is important to keep food out of the bacteria danger zone. This means refrigerating or freezing food promptly after cooking, and reheating food to a safe internal temperature before eating. It is also important to avoid leaving food out at room temperature for more than two hours.
By following these simple steps, you can help to prevent the growth of bacteria and reduce your risk of foodborne illness.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Bacteria Danger Zone
The bacteria danger zone refers to the temperature range between 40F and 140F, in which bacteria can grow and multiply rapidly. This can lead to foodborne illness, which is a major public health concern.
Question 1: What foods are most at risk of bacteria growth?
Foods that are high in protein, such as meat, poultry, seafood, dairy products, and eggs, are most at risk of bacteria growth.
Question 2: How long can food be left out at room temperature before it enters the bacteria danger zone?
Food should not be left out at room temperature for more than two hours.
Question 3: What is the best way to prevent bacteria growth in food?
The best way to prevent bacteria growth in food is to keep it out of the bacteria danger zone. This means refrigerating or freezing food promptly after cooking, and reheating food to a safe internal temperature before eating.
Question 4: What are the symptoms of foodborne illness?
Symptoms of foodborne illness can include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal cramps, fever, and fatigue.
Question 5: What should I do if I think I have foodborne illness?
If you think you have foodborne illness, you should see a doctor right away.
Question 6: How can I reduce my risk of getting foodborne illness?
You can reduce your risk of getting foodborne illness by following these tips:
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water before handling food.
- Cook food to a safe internal temperature.
- Refrigerate or freeze food promptly after cooking.
- Avoid cross-contamination of food.
- Clean and sanitize food contact surfaces.
By following these tips, you can help to prevent the growth of bacteria and reduce your risk of foodborne illness.
For more information on the bacteria danger zone and food safety, please visit the website of the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA).
Tips for Avoiding the Bacteria Danger Zone
The bacteria danger zone is the temperature range between 40F and 140F, in which bacteria can grow and multiply rapidly. This can lead to foodborne illness, which is a major public health concern. By following these tips, you can help to prevent the growth of bacteria and reduce your risk of foodborne illness:
Tip 1: Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water before handling food.
Washing your hands helps to remove bacteria from your skin, which can then be transferred to food. Be sure to wash your hands for at least 20 seconds, and scrub all surfaces of your hands, including your palms, backs of your hands, between your fingers, and under your nails.
Tip 2: Cook food to a safe internal temperature.
Cooking food to a safe internal temperature kills bacteria that may be present in the food. The safe internal temperature for meat, poultry, and fish varies depending on the type of food. For example, ground beef should be cooked to an internal temperature of 160F, while poultry should be cooked to an internal temperature of 165F.
Tip 3: Refrigerate or freeze food promptly after cooking.
Refrigerating or freezing food promptly after cooking helps to prevent the growth of bacteria. Be sure to refrigerate or freeze food within two hours of cooking.
Tip 4: Avoid cross-contamination of food.
Cross-contamination occurs when bacteria from one food is transferred to another food. This can happen when raw meat, poultry, or fish comes into contact with cooked food, or when dirty utensils are used to handle food.
Tip 5: Clean and sanitize food contact surfaces.
Cleaning and sanitizing food contact surfaces helps to prevent the spread of bacteria. Be sure to clean and sanitize all surfaces that come into contact with food, including countertops, cutting boards, and utensils.
Summary of Key Takeaways or Benefits:
- Following these tips can help to prevent the growth of bacteria and reduce your risk of foodborne illness.
- It is important to practice good food safety habits at all times, even when you are not cooking or eating in a restaurant.
- By following these tips, you can help to keep yourself and your family safe from foodborne illness.
Transition to the Article's Conclusion:
By following the tips outlined in this article, you can help to prevent the growth of bacteria and reduce your risk of foodborne illness. Remember, food safety is everyone's responsibility. By working together, we can help to keep our food supply safe.
Conclusion
The bacteria danger zone is the temperature range between 40F and 140F in which bacteria can grow and multiply rapidly. This can lead to foodborne illness, which is a major public health concern. By understanding the bacteria danger zone and following safe food handling practices, we can help to prevent foodborne illness and keep our food safe to eat.
Key points to remember about the bacteria danger zone include:
- Bacteria can double in number every 20 minutes in the danger zone.
- Food should be kept out of the danger zone by refrigerating or freezing it promptly after cooking.
- Hot food should be kept at or above 140F to prevent bacteria growth.
- Food should not be left out at room temperature for more than two hours.
By following these simple tips, you can help to prevent the growth of bacteria and reduce your risk of foodborne illness.
Food safety is everyone's responsibility. By working together, we can help to keep our food supply safe.
How Many Ounces In A Dry Pint? Find Out Here!
Discover Northside Pub And Grill: The Ultimate Local Dining Experience
Ultimate Guide: Finishing Nail Vs. Brad Nail - Everything You Need To Know

Food danger zone stock illustration. Illustration of haccp 85117539

PPT MyPyramid Food Safety Guidelines PowerPoint Presentation, free
THE DANGER ZONE